Advanced Periodontitis Treatment Options You Must Know
Periodontitis is a severe infection of the gums that destroys the periodontal supporting tissue and bone, which support the teeth over a long period. Negligence can result in tooth loss and may compromise overall health. This is because bacteria can contribute to systemic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
The condition of advanced periodontitis should be addressed immediately. At this stage, the infection has become deep-rooted and leads to gum recession or loose teeth. Even patients can also face persistent bad odors and unpleasant bite sensations. This is because severe cases require professional modalities, like:
- Scaling
- Root planing
- Surgical interventions
- Restoration procedures
By understanding the causes and symptoms, patients can make informed decisions and maintain their overall oral health.
Causes of Advanced Periodontitis
The accumulation of plaque mostly causes periodontal disease. Plaque refers to a sticky bacterial film that forms on teeth in cases where oral health is ignored. With the passage of time, the plaque becomes solid and cannot be washed away through mere brushing. The harmful bacteria that accumulate inside tartar irritate the gums and cause inflammation. If left ignored, gingivitis develops into periodontitis and then to advanced periodontal disease. Other contributing factors include:
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Slows down the blood supply in the gums and prolongs healing.
- Genetics: Some are prone to gum disease.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to infection.
- Hormonal Change: Pregnancy and menopause may make gums sensitive.
- Malnutrition: Lack of vitamins in the body deters gum tissue.
When chronic, it can compromise the immune system, making infections harder to overcome
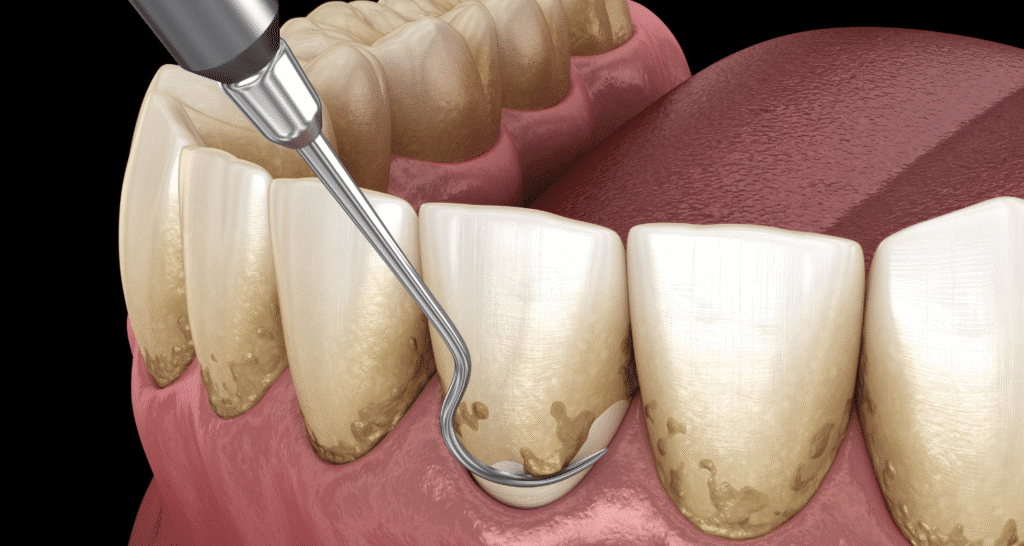
Symptoms of Advanced Periodontitis
It is important to note periodontitis symptoms at the initial stages, as the time lag minimizes complications to the extent that teeth may be lost. Gum disease, in turn, usually starts somewhat discreetly, when it swells, bleeds, and causes a bad odor, which only then develops to such an extreme that essential treatment becomes crucial.
- Swollen, tender, or bleeding gums.
- Receding gums, making teeth appear longer.
- Deep pockets between teeth and gums.
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Loose or shifting teeth.
- Pain while chewing.
- Partial or complete tooth loss in severe cases.
As soon as these symptoms are shown, there is a need to control professional periodontal disease treatment
Oral Hygiene and Prevention
Although advanced cases require care beyond home care, they still prioritize oral hygiene as the primary approach to managing periodontitis. Patients should practice:
- Cleaning the teeth twice a day with a soft-bristle toothbrush is recommended.
- Flossing or interdental brushing helps remove plaque between teeth.
- Antibacterial gum rinses are used to lower the count of bacteria.
- Dental checkups should be done every 6 months to check the health of the gums.
- Lifestyle modifications include quitting smoking and improving dietary habits.
Sometimes, deeper treatment is more costly than prevention. Nevertheless, in case of advanced diabetic bleeding, procedures involving deep cleaning of the gums and other treatments are critical.
Scaling and Root Planing: The First Line of Defense
One of the initial and most necessary methods of treating advanced periodontal disease, a deep cleaning procedure, also known as scaling and root planing, is considered the first solution in removing insidious plaque and tartar deposits and assisting gums in recovering and obtaining a healthier appearance and structure.
- Scaling removes plaque and tartar deposits both above and below the gumline.
- Root planing smooths rough root surfaces, reducing places where bacteria can reattach and allowing the gums to heal better.
This non-surgical therapy allows for a decrease in the level of gum pockets and the management of infection. In some cases, the patient may require more than one session, and antibiotics can be administered to eliminate persistent bacteria.
Professional Treatment Options for Advanced Periodontitis
In case scaling and root planing are not enough to manage infection, dentists can prescribe more periodontal professional treatments, such as surgical and regenerative procedures, to overcome deep periodontal pockets, replace bone support, and maintain the oral health and stability in the long term.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatment involves the use of lasers on the infected tissue and bacteria, sparing healthy tissue.
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): Gums are pulled upwards to cleanse the deep pockets of any tartar, and then the gums are sewn in place to create fewer openings where bacteria feed.
- Bone Grafting: In cases of bone loss due to periodontitis, bone grafting using natural or synthetic materials can restore lost jawbone.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: A sheet is placed between the bone and fibrous tissue, which stimulates bone regeneration.
Soft Tissue Grafts – Gum grafting will correct severe recession and alleviate tooth root sensitivity.
Restorative Solutions: Fixed and Partial Denture Repair
The loss of teeth is a common condition associated with advanced periodontitis, and hence, restorative treatment becomes an important aspect of recovery. The replacement of missing teeth includes restoring chewing capabilities, restoring appearance, preserving the bone of the jaw, and assisting the clients to regain their self-esteem in their overall oral health.
- The use of fixed denture repair helps patients restore their chewing function and improve aesthetics when dentures or dental prosthetics are compromised by gum disease.
- Partial denture replacement is encouraged in cases where teeth are lost due to severe conditions, thus offering a less expensive alternative to tooth replacement, alongside preserving the oral structures.
- Implants can be used on the teeth in cases of bone loss, provided the infection is controlled.
Restorative dentistry is also able to prevent further degeneration of oral tissues by restoring functionality.
Cost of Periodontal Disease Treatment
Treatment of advanced periodontitis has a diverse cost depending on the severity of the disease, the treatment procedures that would be needed, as well as the geographical location; the costs include non-surgical cleanings as well as surgical treatments and restorative dental remedies.
Although treatment would appear expensive, in most instances, failure to treat with any advanced periodontal disease leads to greater costs due to loss of teeth and complex restorations.
How to Treat Periodontitis Effectively
Managing advanced periodontal disease is a challenge that can only be done successfully when a professional intervention and personal dedication accompany it. Although dental care addresses infections and structural issues, future success depends on maintaining careful dental care, modifying lifestyles, and regular follow-ups to ensure gum health.
- Begin with a consultation and full periodontal evaluation.
- Undergo recommended scaling and root planing.
- Consider surgical or laser treatments for deeper pockets.
- Follow strict oral hygiene practices at home.
- Keep up with maintenance appointments to prevent recurrence.
- Restore missing teeth with partial dentures, fixed prosthetics, or implants when appropriate.
The consistency in treatment is the key to long-term success. Patients who actively participate in their treatment have a higher chance of retaining their natural teeth.
Conclusion
Advanced periodontitis is a serious condition that can be treated with patient commitment and effective treatment. Individuals can:
- Manage the disease
- maintain oral health
- Restore function
With scaling and root planing, along with restorative options such as partial or fixed dentures, a variety of professional treatments can be tailored to the patient. Investing in periodontal disease care can help prevent future complications. Future complications can be more expensive and painful.
Patients can achieve healthier smiles and an improved quality of life by combining expert care with diligent oral hygiene. Dental Faith is focused on offering personalized and efficient approaches to deal with advanced periodontal diseases and assist patients in restoring their self-confidence in their bodies.
FAQs
Can you recover from advanced periodontitis?
With appropriate treatment, yes, you can cope and control advanced periodontitis, although not much lost bone or tissue will be regained. Through professional maintenance and care, the progression and maintenance of oral health may be halted.
What is the strongest treatment for periodontitis?
Scaling and root planing, coupled with surgical procedures such as bone grafts and flap surgery, are typically the strongest treatment methods. The procedures remove deep infection, reestablish the support structures, and provide the best opportunity of achieving long-term stability.
When is it too late to treat periodontitis?
There is never too much to spend it late, but treatment will be restricted when the majority of the teeth are loose or when bone loss is extreme. At that stage, interventions such as dentures or implants may be necessary to replace lost teeth and restore function
What is stage 3 advanced periodontitis?
Stage 3 periodontitis is characterized by exposed gums, severe alveolar bone loss, mild tooth mobility, and difficulty chewing. At this level, aggressive treatment plays an essential role in preventing tooth loss and oral disease.
