Types of Dental Fillings for Restoring Your Smile
The health of your teeth is the backbone of overall health, and a filling is one of the most common procedures that you might find in a dentist’s office. Cavities, cracks, and worn-out teeth usually require restoration, and various forms of dental fillings can be used to restore both the functionality and appearance of the teeth. There are too many choices to make, and it is necessary to learn what material can be the most suitable to use; they are based on traditional amalgam and tooth-colored composites.
In this blog, we will discuss everything you should know about dental fillings: the types of materials used, the process involved, and their benefits. This will help you make the right choice for your smile.
What Are Dental Fillings?
Dental fillings are restorative materials that are employed to restore decayed teeth, chipped or otherwise damaged teeth. Once your dentist has removed the affected portion of the tooth, they fill the gap with a substance that replenishes the shape, strength, and functionality of the tooth. This is also referred to as dental restoration.
In addition to the sealing of cavities, fillings also prevent further decay, restore the ability to chew, and hold the teeth in their natural position.
Benefits of Dental Fillings
Dental fillings are considered to be one of the most widely used dental procedures, which contribute to restoring the tooth that is destroyed by decay, wear, or fracture. To take care of your mouth, teeth, and overall dental function, it is essential to understand the various kinds of dental fillings.
- Restoration Function: Restores your ability to speak, bite, and chew.
- Protection From Further Decay: Seals off the cavity against bacteria and food particles.
- Durability: Materials such as gold and ceramic will be durable over a long period of time.
- Aesthetics: Composite resin fillings or porcelain blends are tooth-colored, and they fuse with your teeth.
- Minimally Invasive: The dental bonding fillings that are used today are minimally invasive.
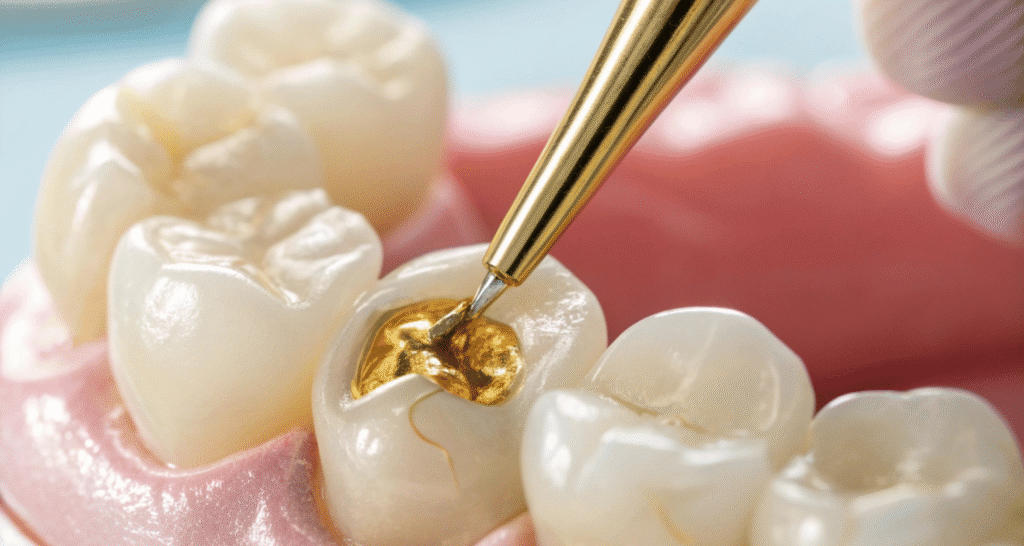
Types of Dental Fillings
Insofar as dental filling types are concerned, there has never been a single solution for all. The decision is based on your tooth situation, esthetics, finances, and even the way your teeth are aligned when you bite. We will consider the most popular ones:
- Amalgam Fillings (Silver Fillings)
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth |
They are also known as silver amalgam fillings, and they are still in use in the posterior molars that do not need cosmetics as much as they require strength.
- Composite Fillings (Tooth-Colored Fillings)
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure |
They are also known as composite resin fillings / composite restorations and are quite popular in terms of cosmetic application.
- Gold Fillings
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure | |
| Gold Fillings | Gold alloy | Extremely durable | Very expensive |
| Premium Restorations | Custom made | Resistant corrosion | Multiple visits |
| Lab crafted | Highly biocompatible | Noticeable appearance |
- Ceramic (Porcelain) Fillings
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure | |
| Gold Fillings | Gold alloy | Extremely durable | Very expensive |
| Premium Restorations | Custom made | Resistant corrosion | Multiple visits |
| Lab crafted | Highly biocompatible | Noticeable appearance | |
| Ceramic Fillings | High-quality ceramic | Natural color | More costly |
| Porcelain Fillings | Porcelain bonded | Stain resistant | Can brittle |
| Durable strong | Long-lasting beauty | Bonding issues |
- Glass Ionomer Fillings
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure | |
| Gold Fillings | Gold alloy | Extremely durable | Very expensive |
| Premium Restorations | Custom made | Resistant corrosion | Multiple visits |
| Lab crafted | Highly biocompatible | Noticeable appearance | |
| Ceramic Fillings | High-quality ceramic | Natural color | More costly |
| Porcelain Fillings | Porcelain bonded | Stain resistant | Can brittle |
| Durable strong | Long-lasting beauty | Bonding issues | |
| Glass Ionomer | Acrylic glass | Fluoride release | Less durable |
| Fluoride Fillings | Mixture material | Bonds directly | Temporary option |
| Protective blend | Cavity prevention | Children teeth |
Glass ionomer fillings are a great preventive measure, particularly in patients who tend to decay.
- Onlays and Inlays (Indirect Fillings)
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure | |
| Gold Fillings | Gold alloy | Extremely durable | Very expensive |
| Premium Restorations | Custom made | Resistant corrosion | Multiple visits |
| Lab crafted | Highly biocompatible | Noticeable appearance | |
| Ceramic Fillings | High-quality ceramic | Natural color | More costly |
| Porcelain Fillings | Porcelain bonded | Stain resistant | Can brittle |
| Durable strong | Long-lasting beauty | Bonding issues | |
| Glass Ionomer | Acrylic glass | Fluoride release | Less durable |
| Fluoride Fillings | Mixture material | Bonds directly | Temporary option |
| Protective blend | Cavity prevention | Children teeth | |
| Indirect Fillings | Custom made | Harder durable | Two visits |
| Inlays Onlays | Lab crafted | Less damage | More costly |
| Cemented tooth | Very precise | Longer process |
The indirect fillings can be of gold, composite, or porcelain and are a combination of durability and aesthetics.
- Temporary Fillings
| Type | What they are | Benefits | Considerations |
| Amalgam Fillings | Blend silver | Long-lasting strong | Noticeable appearance |
| Silver Fillings | Tin copper | Cost-effective durable | Not ideal |
| Mercury mix | Front teeth | ||
| Composite Fillings | Resin mixed | Blend seamlessly | Less durable |
| Tooth-colored Fillings | Glass quartz | Natural teeth | Wears faster |
| Durable material | Visible areas | Heavy pressure | |
| Gold Fillings | Gold alloy | Extremely durable | Very expensive |
| Premium Restorations | Custom made | Resistant corrosion | Multiple visits |
| Lab crafted | Highly biocompatible | Noticeable appearance | |
| Ceramic Fillings | High-quality ceramic | Natural color | More costly |
| Porcelain Fillings | Porcelain bonded | Stain resistant | Can brittle |
| Durable strong | Long-lasting beauty | Bonding issues | |
| Glass Ionomer | Acrylic glass | Fluoride release | Less durable |
| Fluoride Fillings | Mixture material | Bonds directly | Temporary option |
| Protective blend | Cavity prevention | Children teeth | |
| Indirect Fillings | Custom made | Harder durable | Two visits |
| Inlays Onlays | Lab crafted | Less damage | More costly |
| Cemented tooth | Very precise | Longer process | |
| Temporary Fillings | Short-term material | Pain relief | Not permanent |
| Emergency Restorations | Dentist placed | Prevent infection | Multi-visit needed |
| Protective cover | Shields tooth | Nerve exposure |
These fillings are temporary, and they are usually replaced after several weeks.
The Dental Filling Procedure
A dental filling is a simple procedure aimed at eliminating decay and replacing the tooth structure. Using modern techniques and anesthesia, it is fast, painless, and very effective in keeping your natural smile. The following is a step-by-step guide of what is expected:
- Examination and Diagnosis: The Dentist checks the tooth using X-rays when necessary.
- Anesthesia: A local anesthetic is applied to anesthetize the area.
- Decay Removal: The dentist removes the decay.
- Tooth Preparation: Brushing and carving out the cavity.
- Filling Placement: Fillings can be layered, formed, or bonded depending on the material.
- Polishing & Bite Check: The filling is polished, and your bite is checked to ensure it is comfortable.
Which Dental Filling Should You Select?
Several personal and clinical considerations determine the selection of an appropriate filling. Regardless of the location of your cavity or the budget you have for cosmetics or dental care, understanding these factors is crucial for achieving the most successful dental health experience.
- Location of the cavity: Front vs. back teeth.
- Durability needs: Heavy bite pressure may require gold or amalgam.
- Cosmetic preference: Tooth-colored materials like composite or porcelain are better for visible teeth.
- Budget: Amalgam is the most affordable, while ceramic and gold are on the higher end.
- Dental history: Patients prone to cavities may benefit from fluoride-releasing glass ionomer fillings.
Your dentist will assist you in considering these factors and suggest the most appropriate material.
Metal vs. Tooth-Colored Fillings
In the choice between metal and tooth-colored fillings, patients have to strike a balance between durability and aesthetics. Although metal materials such as amalgam and gold are strong, tooth-colored materials such as composite and porcelain give a natural and smooth appearance.
- Metal fillings (gold, amalgam, silver) are considered strong and long-lasting; however, they are easily noticeable.
- Tooth-colored fillings (composite, ceramic, glass ionomer) are a combination of materials, which have an aesthetic benefit but can be potentially detrimental to the longevity of certain fillings.
Conclusion: Restore Your Smile with the Right Filling
One of the best methods to restore teeth that are deteriorated by cavities or trauma is dental fillings. Whether it is silver amalgam to composite resin fillings or gold inlays to porcelain restorations, the correct answer lies in your personal needs and likes as far as your dental requirements are concerned.
In Dental Faith, we provide you with customized attention and deliver maximum results for your smile. You can be assured that our skilled personnel will guide you through each process, whether you require a temporary filling that lasts just a day or a permanent solution, such as a ceramic or gold structure.
Wait, not until a little hole turns into a huge one. Make your reservation at Dental Faith and let us help you smile again with the right dental filling.
FAQs
Which type of filling is best for teeth?
Your requirements will determine the ideal filling. Composite fillings are good when you want an aesthetic look. Amalgam or gold is good when you want a long-lasting filling, and when you want a filling that resists stains, ceramic is a good choice. Practicing dentists will suggest the best alternative depending on the location and cost.
What are the three most common types of filling?
Amalgam (silver), composite resin (tooth-colored), and gold are the most prevalent types. Such materials are the most diverse in terms of durability, cost, and aesthetics in the area of restorative dentistry.
What is the healthiest type of filling?
The composite resin and ceramic fillings are the healthiest as they are biocompatible, free of mercury, and are directly bonded to the teeth. They are functional and retain more natural tooth structure than metal-based options.
What is the new type of filling for teeth?
They are functional, and they retain more natural tooth structure. A more recent option is glass ionomer fillings that release fluoride to prevent future decay. New composite resins and bioactive materials are also emerging, offering superior bonding, aesthetics, and long-term protection.
