
The Importance of Regular Dental X-rays
Dental X-rays look at what’s happening in your mouth without any symptoms. If you’ve ever wondered why X-rays are so necessary, even when we do a great job maintaining our oral health or when under the watchful eye of a great dentist, this blog will help explain the necessity of X-rays. In this article, we will discuss the importance of dental X-rays, their advantages, and how they play a key role in preserving oral health and identifying issues before they become more significant problems.
What Is A Dental X-Ray?
A dental X-ray is like a special camera that captures images inside our mouth using invisible radiation to see our teeth and jaws. These images provide important information about our oral health, enabling our dentist to detect and resolve potential problems before they become bigger. X-rays can provide an all-encompassing view of our teeth, gums, and jawbone that is sometimes not visible during a regular check-up alone.
Types Of Dental X-Rays
Several dental X-rays are used, each for specific information about your oral health. Types of Dentists and Their Roles in Healing Dental Problems
Bitewing X-rays
One of the most common is a bitewing X-ray. These photos show the upper and lower back teeth making contact. Dentists use bitewing X-rays to check for cavities between teeth that might not be seen in a routine dental exam. They also help identify the loss of bone caused by gum disease.
Periapical X-rays
Periapical X-rays show a detailed view of an entire tooth, from the crown to the root and the surrounding bone. They are especially valuable in diagnosing problems below the gum line, including abscesses, cysts, or bone changes.
Panoramic Dental X-rays
Panoramic X-rays show a broad view of your mouth, both upper and lower, and are used to show the entire mouth in one image, including all of a person’s teeth, the upper and lower jaws, as well as the surrounding areas, such as the nasal area and sinuses. This radiograph helps identify impacted wisdom teeth, jaw disorders, and tumors. It is commonly practiced in orthodontic planning and when practicing a significant dental procedure.
Occlusal X-rays
Occlusal X-rays are more significant and show the floor or roof of the mouth. X-rays substantially contribute to monitoring tooth growth and position in young patients. Dentists employ them to find the presence of extra teeth, jaw fractures, or cleft palate problems.
Full-Mouth X-rays (FMX)
This type of X-ray includes a set of multiple X-rays covering all teeth and structures in the surrounding area. This full-mouth radiographic set is usually taken for new patients and provides a broad base of future care.
Cephalometric X-rays
Cephalometric X-rays are taken from the side of the face and jaw. Orthodontists often use these images to analyze the relationship between teeth and jaw growth and alignment.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography
A cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan generates three-dimensional images that show your teeth, bones, and soft tissues in great detail. This high-end software is often used for implant planning, orthodontic evaluation, and diagnosing complex dental conditions.
All types of dental X-rays help your dentist gain the information he needs to customize treatment. These images provide a means to ensure a proper diagnosis and for targeted and efficient care, maintaining proper oral health throughout life stages.
Why Do Dentists Perform Dental X-rays?
If you go for regular check-ups and see the dentist’s detective work with X-rays, you will get an explanation of what a condition looks like and how to fix it. Dental X-rays serve several purposes that are important in a dental setting:
- Identifying cavities or tooth decay
- Examining the potential issues with wisdom teeth
- Evaluating bone levels
- Assessing the root and pulp health
- Tracking dental development
- Guiding Treatments
How Does A Dental X-ray Work?
Dental X-rays are similar to traditional medical X-rays in their use. A unidirectional beam of electromagnetic radiation is aimed at your teeth and jaws. This radiation penetrates soft tissues, like gums, but is partially absorbed by denser structures, like teeth and bones. When the radiation reaches these structures, it exposes a digital sensor or film to produce an image. Consider the following points:
- Radiation: Dental X-rays use a tiny amount of radiation, so their regular use is safe.
- Image creation: The different densities of soft and hard tissues allow dentists to view details not visible to the naked eye.
- Image Interpretation: Analysis of X-Ray Image By Paraphrased Text: Dentists use X-ray images for diagnosis and treatment planning.
How Often Do I Need A Dental X-ray?
What Is the Best Dentist X-ray Frequency? The commonly preferred frequency is once every six months. X-rays are advised, for most, every year during check-ups. Your dentist may suggest getting more X-rays if you have certain concerns or treatment in progress.
- Age: More X-rays are usually needed for children to monitor the growth of permanent teeth and proper alignment.
- Oral Health History: Patients with cavities, gum disease, or other dental conditions may require more regular imaging.
- New Patients: If you’re visiting a dental office for the first time, initial X-rays provide a complete picture of your oral health.
- Routine Treatments: Additional X-rays may be needed to monitor the progress of specific treatments (such as braces or implants).
By using educated technology and collecting images, we complete risk-free X-rays with minimal radiation so that you can carry out your diagnosis and treatment plan.
Are There Side Effects of Dental X-rays?
Dental X-rays are safe and use a very low dose of radiation. Many dental practices use digital X-rays that lower radiation exposure even more than traditional film X-rays. While the likelihood of exposure is subtle, care is taken to avoid it, with lead aprons and thyroid collars offering protection against excess dosage of patients.
- Pregnancy: Although dental X-rays are generally safe, pregnant patients should let their dentist know to take extra precautions or delay nonessential X-rays.
- Sensitivity to Radiation: These patients could benefit from alternative imaging techniques or extra shielding.
How Dentists Use X-rays To Plan Treatments
The purpose of dental X-rays is key to accurate, effective, and personalized treatment planning. X-rays provide in-depth perspectives of otherwise unobservable areas, enabling dentists to make informed decisions for better treatment outcomes. Here’s how they are involved in different facets of treatment:
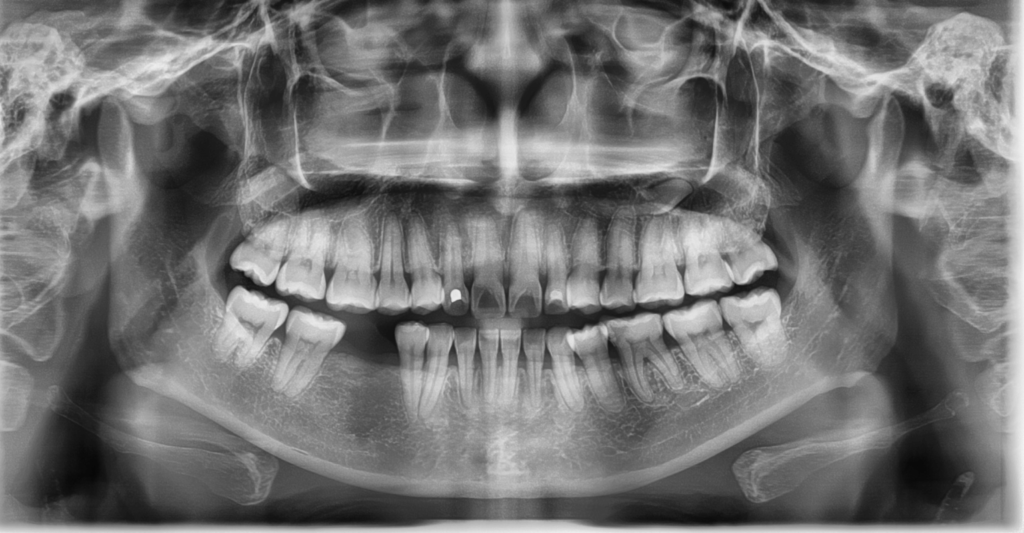
Pinpointing Decay and Damage
Dental X-rays are essential for detecting cavities, cracks, or decay in locations that are difficult to see during a visual exam, like between teeth, below the gums, and under existing restorations. Identifying these problems while they are still in their infancy allows us to intercept the progression of dental disease and can be potentially life-saving to avoid more extensive and costly procedures later on.
Evaluating the Bone Underpinning Tooth Prostheses
When patients are contemplating dental implants, X-rays are crucial for determining jawbone density and health. 3D Panoramic and Cone beam computer tomography (CBCT) Scans—The more detailed 3D images of the bone structure provided by these scans help your dentist determine whether you have enough bone to support an implant or if additional procedures like bone grafting are required.
Custom Orthodontic Interventions
Further implications of the present invention can be utilized in orthotics, including X-rays based on careful analysis of cephalometric and panoramic images. These “photographs” show the alignment of the teeth, how the jaws relate to one another, and any structural issues within. Dentists and orthodontists can use the information to create personalized treatment plans like braces or aligners targeting each patient’s needs.
Monitoring Periodontal Health
In the case of periodontal disease, dental X-rays are often used to assess bone loss around the teeth. This is important to plan periodontal management, such as scaling and root planing or even surgery. X-rays also help dentists track healing after the first treatment to guarantee long-term success.
Root Canals For Identifying Impactions & Cysts
Dental X-rays, particularly panoramic radiographs, are essential in identifying impacted teeth, cysts, and other abnormalities that might complicate treatment. Radiographs are used to identify and assess impacted mandibular and maxillary third molars to examine the area in preparation for possible extraction.
Ensuring Long-Term Success
Dental X-rays also track how well prior treatments, like fillings, crowns, or implants, have worked. These advancements enable dentists to detect early signs of complications and take timely action to ensure restoration of teeth is healthy and functional.
Trust Dental Faith for Your Radiographs
We know how essential it is to get precise and dependable imaging for your oral health at Dental Faith, with advanced technology that provides high-resolution imaging comfortably and safely. Our trained dental team is needed for routine annual X-rays, radiographs, full mouth series, etc.
For new patients, we typically take a complete series of X-rays so that our team fully understands your oral health. This information is the baseline to help us tailor treatments to your needs and guide you to a healthy smile.
Are you ready for the next step in your oral health journey? Get More information about our state-of-the-art imaging technology and schedule your new patient appointment today! At Dental Faith, we want to help you to have a beautiful, healthy smile and keep it!
FAQs
What are the three types of dental X-rays?
Three common types of dental X–rays are bitewing X–rays (to check for cavities), periapical (to see the whole tooth, as well as the surrounding bone), and panoramic (to take a broad view of the entire mouth).
How often is it safe to get dental X-rays?
Taking a dental X-ray annually or as needed is considered safe, as the radiation exposure is limited and extremely well-controlled with current technologies.
What do dental X-rays cost?
Prices for dental X-rays vary widely, typically costing between $25 and $250 and depending on the type (bitewing, panoramic, etc.) and insurance coverage.
How often should you get dental X-rays in ADA?
Dental X-rays should be taken according to your specific needs, as detailed in the ADA guidelines, usually every 6-24 months, depending on your age, oral health, and risk factors.
